
RevOps Overview
Revenue Operations (RevOps) is essential for aligning marketing, sales, customer success, and other revenue-generating functions to optimize business growth. This blog will explore the key components of RevOps and how it should integrate with your revenue strategy.
What is Revenue Operations?
RevOps is the strategic alignment of teams, processes, and technology to break down silos and create a unified approach to revenue generation. It enhances collaboration, accountability, and efficiency, ensuring all departments work toward common revenue goals.
The RevOps Model vs. the Operating Model
An Operating Model represents how a company delivers value internally and externally, mapping processes across departments to drive efficiency. A RevOps Model focuses on revenue generation by integrating marketing, sales, and customer success operations.
Key Differences: RevOps Model vs. Operating Model
| Aspect | RevOps Model | Operating Model |
| Focus | Revenue generation and alignment of sales, marketing, and customer success. | Overall business structure and value delivery across all functions. |
| Objective | Streamline revenue-related processes, break silos, and improve efficiency. | Define how the company operates to create and deliver value. |
| Scope | Customer-facing and revenue-generating functions. | Broad, covering all departments, including HR, finance, and supply chain. |
| Key Components | Strategy, data, workflows, processes, technology, analytics. | Business strategy, organizational structure, processes, governance. |
| Technology Use | Integrates sales, marketing, and customer success tools for revenue optimization. | Covers enterprise-wide technology and infrastructure. |
| Measurement | Revenue growth, sales efficiency, customer lifecycle success. | Business performance, operational efficiency, and value chain optimization. |
In essence, the Operating Model defines how a company functions to deliver value, while the RevOps Model focuses on aligning revenue-driving teams and processes for optimal revenue performance.
Key Attributes of a RevOps Model Framework:
- End-to-End Customer Lifecycle Support – Aligns marketing, sales, and customer success to create a seamless customer journey.
- Integrated Workflows & Data – Ensures smooth cross-functional collaboration with shared data and interconnected processes.
- Strategic Alignment – Unifies revenue objectives across all departments to drive predictable growth.
- Technology & Automation – Leverages integrated tech stacks to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
- Revenue Process Visibility – Provides real-time insights into revenue execution and performance metrics.
- Accountability & Governance – Establishes clear ownership of processes, tools, and revenue-driving activities.
- Continuous Optimization – Uses data-driven decision-making to refine strategies, improve performance, and maximize revenue.
A strong RevOps framework breaks down silos, enhances collaboration, and ensures every function contributes to sustainable revenue growth.
RevOps Framework Components
- Strategy – Aligns revenue goals with operational execution to drive growth.
- Data & Analytics – Centralizes data for better decision-making, performance tracking, and optimization.
- Workflows & Processes – Establishes streamlined, automated, and scalable operations across teams.
- Technology – Integrates tools and systems to enhance efficiency and collaboration.
- Revenue Performance Management – Monitors key metrics to measure and improve revenue outcomes.
- Change Management & Enablement – Ensures smooth adoption of new processes, tools, and best practices.
Why RevOps Works
Traditional business structures often create inefficiencies due to siloed departments. RevOps eliminates these barriers, fostering accountability and streamlined operations. A well-implemented RevOps framework provides a holistic view of revenue growth, ensuring optimal decision-making and maximizing profitability.
Next Steps
Building a RevOps framework requires time and effort, but the benefits—efficient operations, aligned teams, and a scalable revenue engine—make it a worthwhile investment.
Now let us do a deeper dive:
Key Functions of RevOps
RevOps align Sales, Marketing, and Customer Success by eliminating silos and ensuring seamless information flow. We achieve this through:
- Unified metrics across teams
- Building trust and accountability
- Defining ownership of the tech stack
- Effective change management
A 360° RevOps approach leverages technology and data to drive revenue growth and enhance collaboration, keeping customers at the core of all processes.
Core Responsibilities of a RevOps Team
- Removing Sales Roadblocks – Eliminating obstacles that hinder coordination and revenue generation.
- Operations Management – Optimizing business processes and policies for efficiency.
- Data Analytics & Insights – Utilizing data to improve engagement and workflows.
- Compliance & Regulation – Ensuring adherence to organizational and legal standards.
- Technology Implementation – Managing software procurement, integration, and maintenance.
- Learning & Development – Training employees on new revenue systems.
- Enhancing Collaboration – Driving transparency and accountability across all levels.
Building a revenue operations (RevOps) team from the ground up can appear daunting, as integrating it into a previously siloed organization presents challenges.
You must evaluate the current needs, strategy, and budget and consider the company culture, as this will shape department growth. Key considerations include the reporting structure—RevOps reporting to the CFO, COO, or CRO. Let’s focus on the practical constraints affecting RevOps structure from startups to enterprises to outline the ideal organizational model independent of external influences.
I wrote a blog earlier on building a RevOps team to discuss the roles and skills required for an effective RevOps team. In SMBs, RevOps structures vary based on growth stage, team size, and revenue complexity. Below is a breakdown of how RevOps functions evolve from Early-Stage Startups (1-50 employees) to Mid-Market Companies (200-500 employees) to Enterprise Companies (+500 employees).
Early-Stage Startup (1-50 employees, <$10M ARR)
RevOps Model: One-Person Generalist or Founder-Led Ops
At this stage, there is typically no dedicated RevOps team. Instead:
- Founder(s), COO, or Head of Sales/Marketing handles RevOps tasks.
- A RevOps Generalist (if hired) manages CRM, reporting, and process automation.
- The focus is on setting up scalable processes for lead generation, pipeline tracking, and basic automation.
- Sales, marketing, and CS share tools (e.g., SalesForce for CRM & automation).
- Minimal forecasting—revenue projections are often based on gut feel & spreadsheets.
Key Roles (if any):
RevOps Generalist (handles sales, marketing, and customer success ops)
Founder/COO-led RevOps (if no dedicated hire)
Common Tools:
Hubspot/Zoho (CRM & marketing automation)
Google Sheets / Airtable (forecasting)
Zapier (automation)
Challenges:
Lack of data hygiene and process standardization
Poor sales & marketing alignment on the lead handoff
Difficult to track the ROI of marketing efforts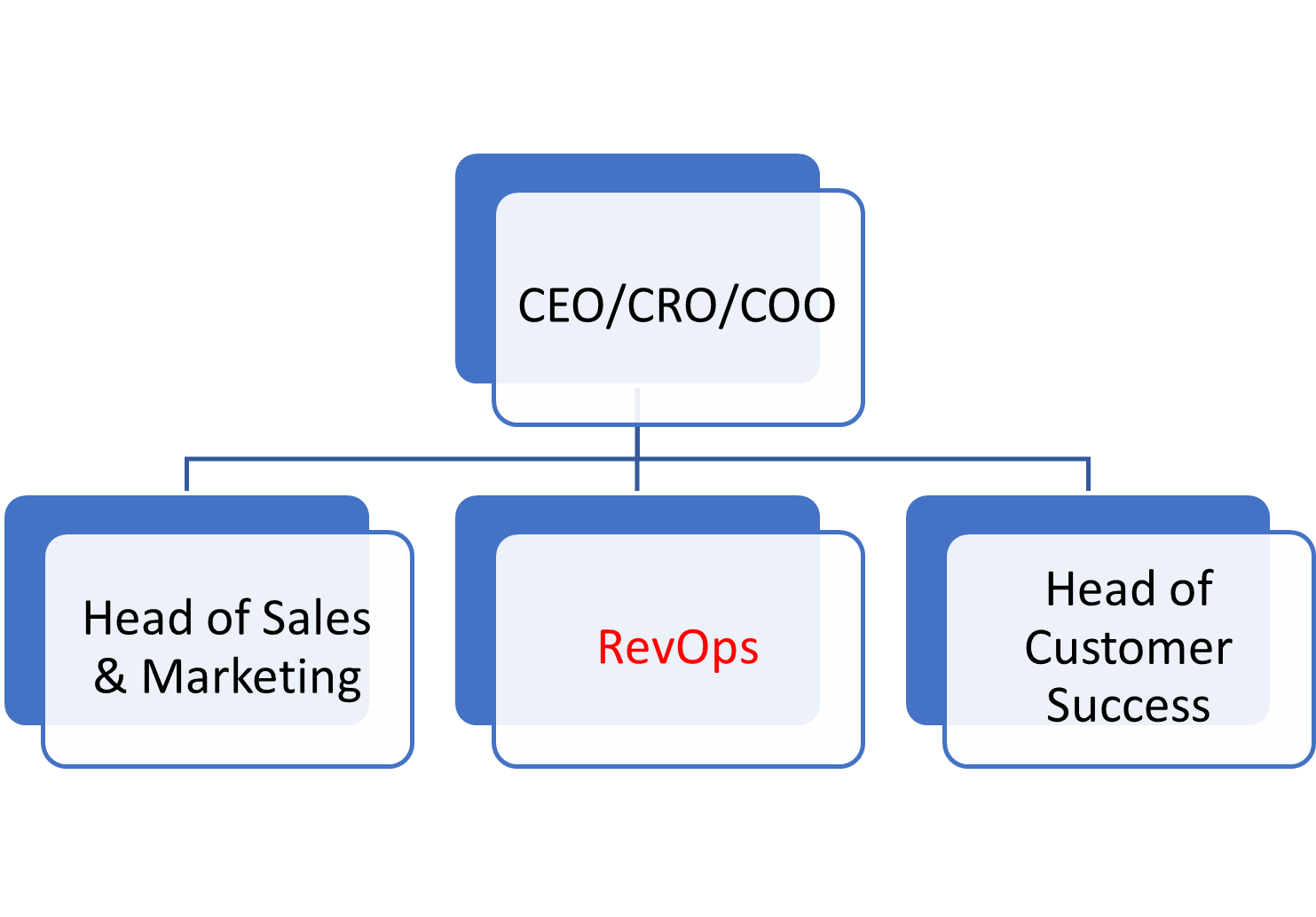
Growth-Stage SMB (50-200 employees, $10M-$50M ARR)
RevOps Model: Small RevOps Team (2-3 People)
RevOps becomes a formal function at this stage, often led by a RevOps Manager or Director reporting to the CRO, COO, or VP of Sales.
- CRM complexity increases (moving from HubSpot/Zoho to Salesforce).
- Separate SalesOps and MarketingOps roles emerge.
- Revenue forecasting becomes data-driven instead of gut feel.
- Increased automation and integration between tools.
- First customer success ops hire (if retention & expansion are key).
- RevOps focuses on lead-to-revenue optimization and attribution tracking.
Key Roles:
RevOps Manager (or Director) – Oversees GTM alignment, reporting, & systems.
SalesOps Specialist – Manages CRM, sales process, forecasting
MarketingOps Specialist – Owns automation, lead routing, attribution
CSOps (optional) – Focuses on renewals, churn prevention
Common Tools:
Salesforce (CRM)
Marketo or HubSpot (Marketing Automation)
Outreach / Salesloft (Sales Engagement)
Gong (Revenue Intelligence)
Looker / Tableau (Reporting & Analytics)
Challenges:
Need for cross-functional data integration (sales, marketing, CS)
Growing complexity in attribution and forecasting models
Change management as teams adopt new tools & processes.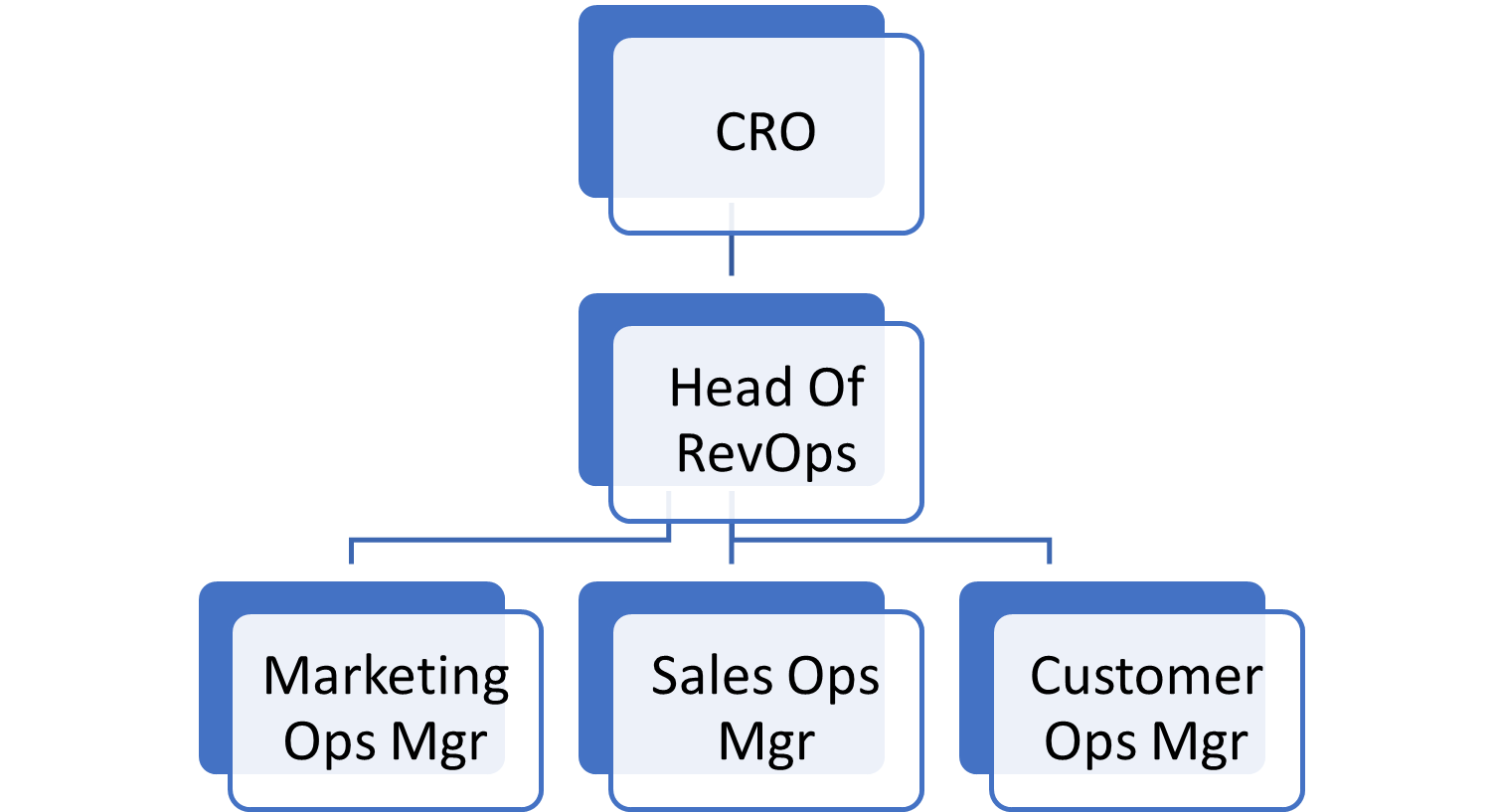
Mid-Market SMB (200-500 employees, $50M-$100M ARR)
RevOps Model: Specialized RevOps Team (5+ People)
RevOps is a fully built-out team with clear functional ownership at this stage.
- RevOps reports directly to the CRO or COO.
- Dedicated teams for SalesOps, MarketingOps, and CSOps.
- Revenue forecasting is predictive and AI-driven.
- RevOps supports territory planning, comp structures, & efficiency improvements.
- Data & reporting functions become more sophisticated (BI tools, SQL-based reporting).
- Heavy focus on scalability, efficiency, and automation.
Key Roles:
RevOps Director (or VP) – Owns overall strategy & executive alignment.
SalesOps Manager & Analysts – Forecasting, CRM management, process automation
MarketingOps Manager & Specialists – Attribution, ABM, funnel optimization
CSOps Lead – Churn reduction, health scores, NPS tracking
RevOps Analyst – Data governance, dashboards, analytics
Common Tools:
Salesforce (CRM) + Full RevOps Tech Stack
Revenue Intelligence (Clari, Gong, or Chorus)
CPQ Software (Conga, DealHub)
BI Tools (Looker, Snowflake, Tableau)
Challenges:
Scaling RevOps processes globally
As functions grow, they create Departmental Silos.
Change management with frequent system upgrades
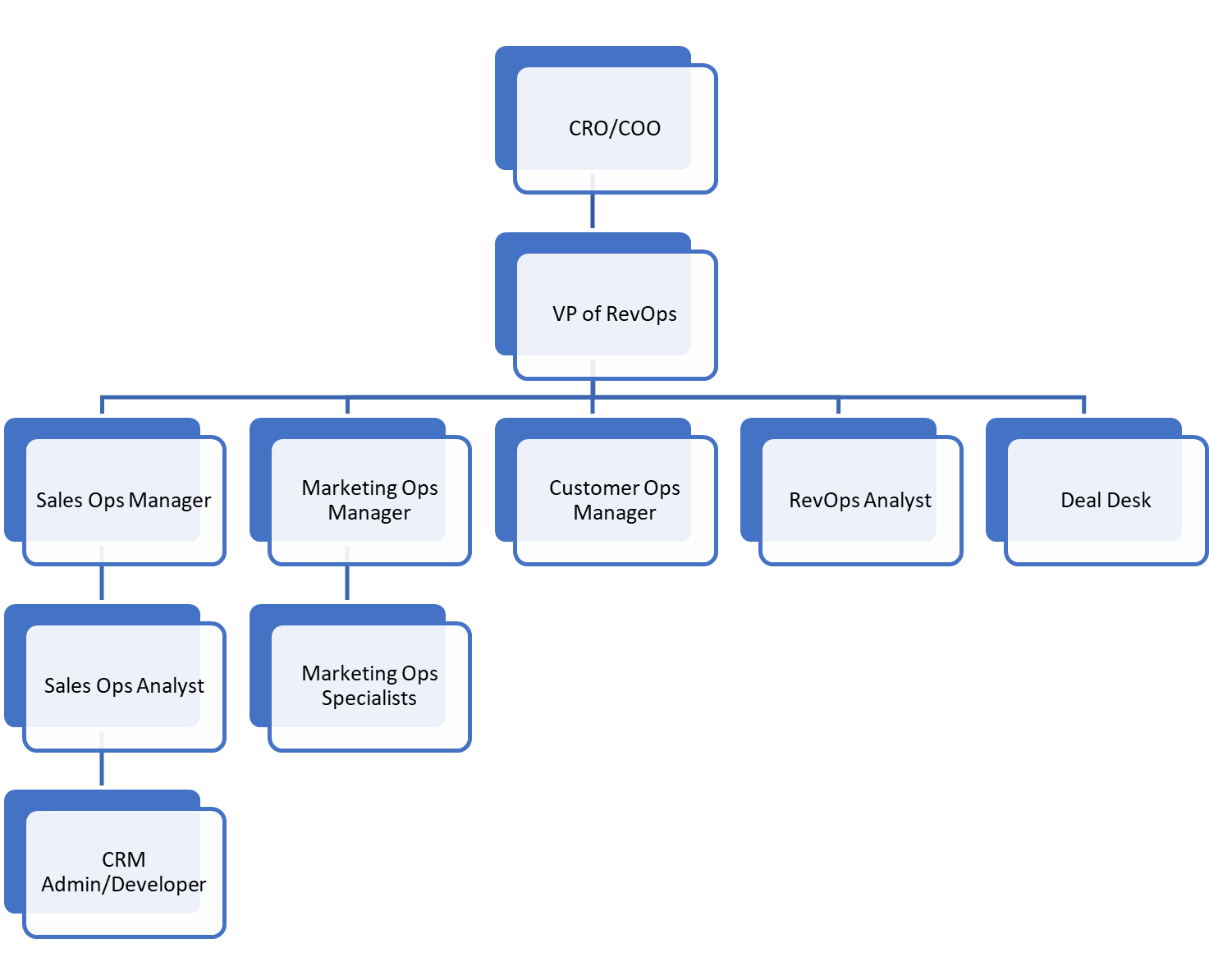
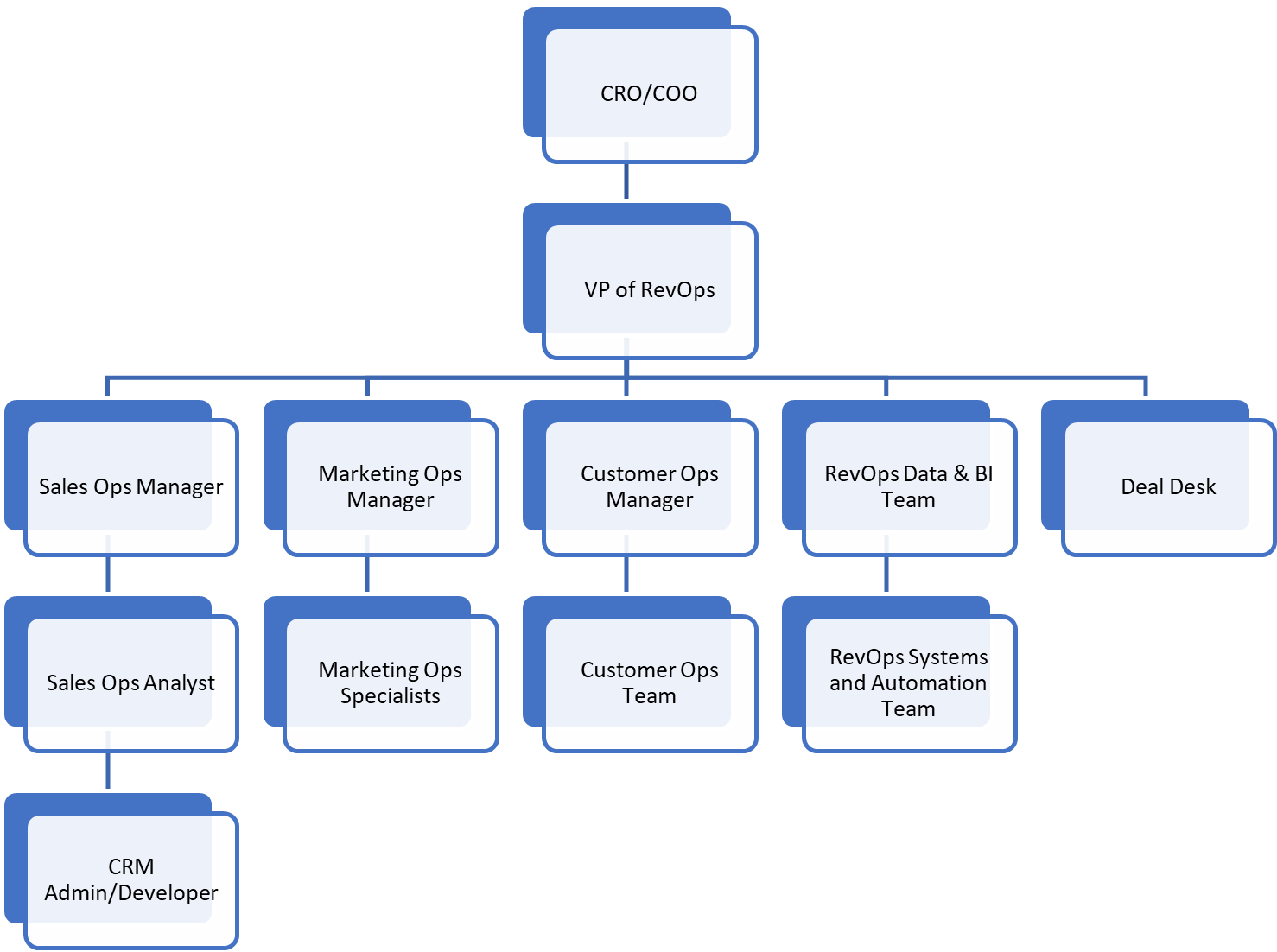
Enterprise (500+ employees, $100M+ ARR)
RevOps Model: Enterprise-Scale RevOps Department (10-50+ People)
- RevOps is a core strategic function, reporting directly to the CRO, CFO, or COO.
- Highly specialized teams for SalesOps, MarketingOps, CSOps, and Revenue Analytics.
- Revenue forecasting is AI-driven and uses advanced predictive models.
- Dedicated RevOps R&D and Innovation teams to drive continuous improvement.
- Global alignment of sales territories, quotas, and revenue reporting.
Key Roles:
VP of Revenue Operations – Oversees global RevOps strategy.
SalesOps Director & Analysts – Manages sales tech stack, territory design, and process efficiency.
MarketingOps Director & Specialists – Owns ABM, multi-channel attribution, and demand gen analytics.
CSOps Director & Teams – Focuses on customer retention, expansion, and lifecycle optimization.
RevOps Data & BI Team – Owns analytics, dashboards, predictive forecasting
RevOps Systems & Automation Team – Oversees CRM architecture, automation, and integrations
Common Tools:
Salesforce Enterprise (CRM)
Marketo / Pardot (Enterprise Marketing Automation)
Clari / BoostUp (Revenue Forecasting)
Gainsight (Customer Success)
Snowflake / Tableau / Power BI (Data & Analytics)
Challenges:
Managing global RevOps alignment across different regions.
Data silos across multiple business units.
Scaling automation & AI-driven insights across large teams.
Ensuring RevOps innovation to keep up with evolving GTM models.
RevOps Evolution Summary by Company Size
| Company Size | RevOps Model | Key Focus | Primary Challenges |
| 1-50 employees | Founder-led or 1-person RevOps | Basic CRM & automation | No structured RevOps, data issues |
| 50-200 employees | Small RevOps Team (2-3 people) | CRM optimization, forecasting, automation | Data integration, lead handoff, tech adoption |
| 200-500 employees | Dedicated RevOps Team (5+ people) | Predictive analytics, GTM strategy, scale ops | Change management, process complexity, silos |
| 500+ employees | Enterprise RevOps Department (10-50+ people) | Global revenue alignment, AI-driven forecasting | Siloed data, global process consistency, advanced automation |
For startups & SMBs, RevOps is a lean function focused on foundational processes and automation. As companies scale into mid-market and enterprise, RevOps becomes highly specialized, focusing on AI-driven forecasting, data governance, and global revenue strategy.
Why a RevOps Framework is needed
- Breaks Down Silos – Aligns sales, marketing, and customer success, ensuring seamless collaboration and shared objectives.
- Improves Efficiency – Streamlines workflows, automates processes and eliminates redundancies to enhance productivity.
- Enhances Data-Driven Decision-Making – Centralizes data to provide actionable insights for revenue growth and performance optimization.
- Increases Accountability – Establishes clear ownership of revenue-driving activities, fostering transparency and responsibility.
- Optimizes Technology & Processes – Integrates tools and systems for a unified approach to managing revenue operations.
- Drives Revenue Growth – Aligns strategies and execution to maximize revenue potential and scalability.
By creating a holistic, data-driven approach, RevOps ensures that organizations operate efficiently, adapt quickly, and sustain long-term growth.
Final Thoughts
For startups & SMBs, RevOps is a lean function focused on foundational processes and automation. As companies scale into mid-market and enterprise, RevOps becomes highly specialized, focusing on AI-driven forecasting, data governance, and global revenue strategy.

Leave a Reply